社会资本对初次创业决策可行性感知的影响研究
浙江财经学院硕士学位论文I摘要已有研究表明,创业决策可行性感知是创业行为实施的关键。目前学术界关于创业决策的研究有限,且多聚焦于个性特质和宏观环境视角,缺乏对社会资本这一影响因素的详细阐述,因此有必要深入探讨社会资本在创业决策中的作用,分析社会资本对创业决策可行性感知的影响机理。为此,本研究以创业者个体为研究对象,选择初次创业情境,详细分析了社会资本对创业决策可行性感知的直接和间接影响,检验了创业自我效能感的中介作用,构建了基于社会资本和认知视角的创业决策过程模型。研究主要采用了文献研究、访谈和问卷调查三种方法。首先,通过文献研究得出,个体的社会资本主要包括结构和关系两个层次及网络规模、网络差...
相关推荐
-
建筑工程投标文件范本-(格式)VIP免费

 2024-11-22 48
2024-11-22 48 -
疾病预防控制中心招标文件VIP免费

 2025-01-09 50
2025-01-09 50 -
体育健身中心施工招标文件VIP免费

 2025-01-09 32
2025-01-09 32 -
江西丰城电厂及广东从化事故案例分析VIP免费

 2025-03-04 7
2025-03-04 7 -
钢结构节点图集CAD版(可编辑)VIP免费

 2025-03-04 20
2025-03-04 20 -
[青岛]精品工程亮点做法图片集(130页)VIP免费

 2025-03-04 12
2025-03-04 12 -
外墙外保温工程技术规程JGJ144-2019VIP免费

 2025-03-04 11
2025-03-04 11 -
地铁停车场施工组织设计VIP免费

 2025-03-04 14
2025-03-04 14 -
项目建设安全管理流程图汇编VIP免费
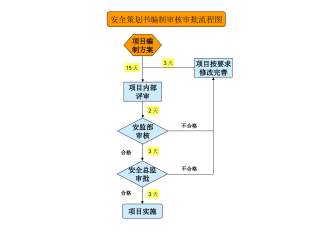
 2025-03-04 34
2025-03-04 34 -
特训班学习心得VIP免费

 2025-03-04 10
2025-03-04 10
作者详情
相关内容
-

[青岛]精品工程亮点做法图片集(130页)
分类:行业资料
时间:2025-03-04
标签:建筑工程、精品工程、细部节点做法、亮点做法
格式:PPT
价格:5 积分
-

外墙外保温工程技术规程JGJ144-2019
分类:行业资料
时间:2025-03-04
标签:外墙保温、工程、规范
格式:ZIP
价格:2 积分
-

地铁停车场施工组织设计
分类:行业资料
时间:2025-03-04
标签:地铁、场段、施工组织设计
格式:DOCX
价格:3 积分
-

项目建设安全管理流程图汇编
分类:行业资料
时间:2025-03-04
标签:安全管理、流程图
格式:PPT
价格:1 积分
-

特训班学习心得
分类:行业资料
时间:2025-03-04
标签:拓展培训、结构化思考、培训、心得体会
格式:DOCX
价格:1 积分